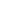
Pulmonary edema is a condition of pathology in the extravascular fluid accumulation in the lungs. The disorder is caused by two circumstances, namely:
- Increased hydrostatic pressure.
- Increased pulmonary capillary permaebilitas.
Symptoms and Signs
- Jugular venous distention, Increased central venous pressure.
- Increased blood pressure, pulse full, strong.
- Slowing time emptying the veins hands.
- Peripheral and periorbital edema.
- Ascites, pleural effusion, acute pulmonary edema (dyspnea, tachypnea, crackles wet throughout the lung fields)
- Rapid weight gain: the addition of 2% = excess light, the addition of 5% = excess medium, addition of 8% = overweight.
Assessment for Pulmonary Edema
1. Pulmonary System
- Subjective: shortness of breath, chest distress, whiny.
- Objective: nostril breathing, hyperventilation, cough (productive / nonproductive), sputum lot, use a respirator muscles, diaphragm and abdominal breathing increases, increased respiratory rate, audible stridor, crackles in the lung fields.
- Subjective: headache.
- Objective: increased pulse rate, blood vessel vasoconstriction, decreased blood quality, irregular heartbeat, extra heart sounds.
- Subjective: restlessness, loss of consciousness, seizures.
- Objective: GCS decreased, reflexes decreased / abnormal, lethargy.
- Subjective: weak, tired.
- Objective: decreased muscle tone, muscle pain / normal, retraction of the lung and respiratory muscle use accessories.
- Subjective: -
- Objective: pale skin, cyanosis, turgor decreases (due to dehydration secondary), a lot of sweat, skin temperature increases, redness.
- Objective: decreased urine production / normal.
- Subjective: nausea, sometimes vomiting.
- Objective: normal stool consistency / diarrhea.
Nursing Diagnosis for Pulmonary Edema
- Ineffective airway clearance r / t intubation, ventilation, process of disease, weakness and fatigue.
- Impaired gas exchange r / t secretion restrained, disease processes, or ventilator setting is not appropriate.
- Impaired verbal communication r / t endotracheal tube installation.
- Risk for infection r / t endotracheal tube installation.